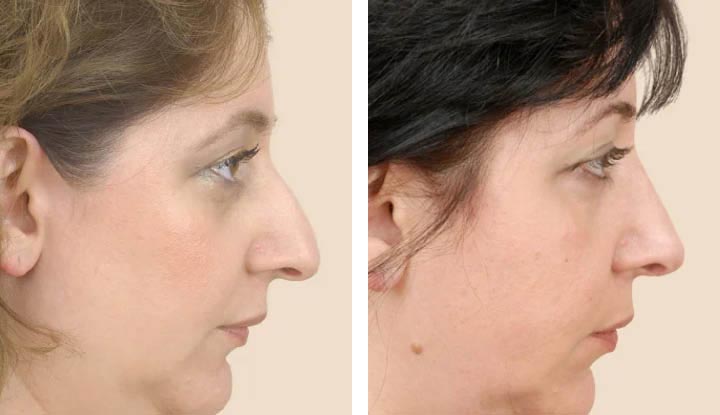
Nose surgery, also known as rhinoplasty, is one of the most common and transformative cosmetic procedures. It offers individuals the opportunity to enhance their facial harmony and improve breathing functionality بهترین جراح بینی تهران کیه. This guide delves into the different aspects of nose surgery, including its types, benefits, risks, and the recovery process.
Types of Nose Surgery
- Cosmetic Rhinoplasty:
- Reduction Rhinoplasty: This procedure reduces the size of the nose, addressing issues such as a prominent hump, wide nostrils, or a bulbous tip.
- Augmentation Rhinoplasty: Used to increase the size of the nose, often using cartilage grafts from other parts of the body, for individuals with a flat or under-projected nose.
- Ethnic Rhinoplasty: Tailored to preserve the unique nasal features of various ethnic groups while making desired adjustments.
- Revision Rhinoplasty: A secondary procedure for patients who are unsatisfied with the results of their initial surgery.
- Functional Rhinoplasty:
- Septoplasty: Corrects a deviated septum, which can obstruct airflow and cause breathing difficulties.
- Turbinate Reduction: Reduces the size of the turbinates (structures inside the nose) to improve airflow.
- Nasal Valve Surgery: Repairs collapsed or narrow nasal valves to enhance breathing.
Benefits of Nose Surgery
- Enhanced Appearance: Rhinoplasty can significantly improve facial symmetry and aesthetics, boosting self-confidence and self-esteem.
- Improved Breathing: Functional nose surgery can alleviate breathing problems caused by structural issues within the nose.
- Correcting Trauma: Rhinoplasty can repair nasal deformities resulting from injury or accidents.
- Addressing Birth Defects: Congenital issues such as cleft palate or nasal malformations can be corrected through surgery.
Risks and Considerations
As with any surgical procedure, rhinoplasty carries certain risks and considerations:
- Anesthesia Risks: Complications from anesthesia are rare but possible.
- Infection: Post-surgical infections, although uncommon, can occur.
- Bleeding: Some bleeding is normal, but excessive bleeding can be a complication.
- Scarring: Scarring is typically minimal and hidden, but it can be more prominent in some cases.
- Asymmetry: Achieving perfect symmetry is challenging, and minor asymmetries may remain.
- Revision Surgery: Some patients may require additional surgeries to achieve their desired results.
The Procedure
- Consultation: The process begins with a thorough consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon to discuss goals, expectations, and medical history.
- Preparation: Patients are advised to avoid certain medications, cease smoking, and follow specific pre-operative instructions to minimize risks.
- Surgery: Rhinoplasty is usually performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon makes incisions either inside the nostrils (closed rhinoplasty) or across the columella (open rhinoplasty) to access the underlying structures.
- Reshaping: The surgeon reshapes the nasal bones and cartilage to achieve the desired contour and correct any functional issues.
- Closing: Incisions are closed, and a splint is applied to support the new shape during healing.
Recovery
- Initial Recovery: Patients can expect swelling, bruising, and discomfort for the first few days. Cold compresses and pain medications can help manage these symptoms.
- Splint and Stitches: The nasal splint and stitches are typically removed after one week.
- Swelling and Healing: Swelling gradually subsides over several months, with the final results becoming more apparent as the nose heals fully.
- Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments with the surgeon ensure proper healing and address any concerns.
Nose surgery is a powerful tool for enhancing facial aesthetics and improving respiratory function. With advancements in surgical techniques, rhinoplasty has become safer and more effective, offering patients a high level of satisfaction.